Terrorist roadblocks strangle the economies of Mali and its neighbours
JNIM’s blockades have become a strategic weapon that threatens regional commerce and the Malian army, and harms civilians.
Published on 06 October 2025 in
ISS Today
By
Hassane Koné
Senior Researcher, ISS Regional Office for West Africa and the Sahel
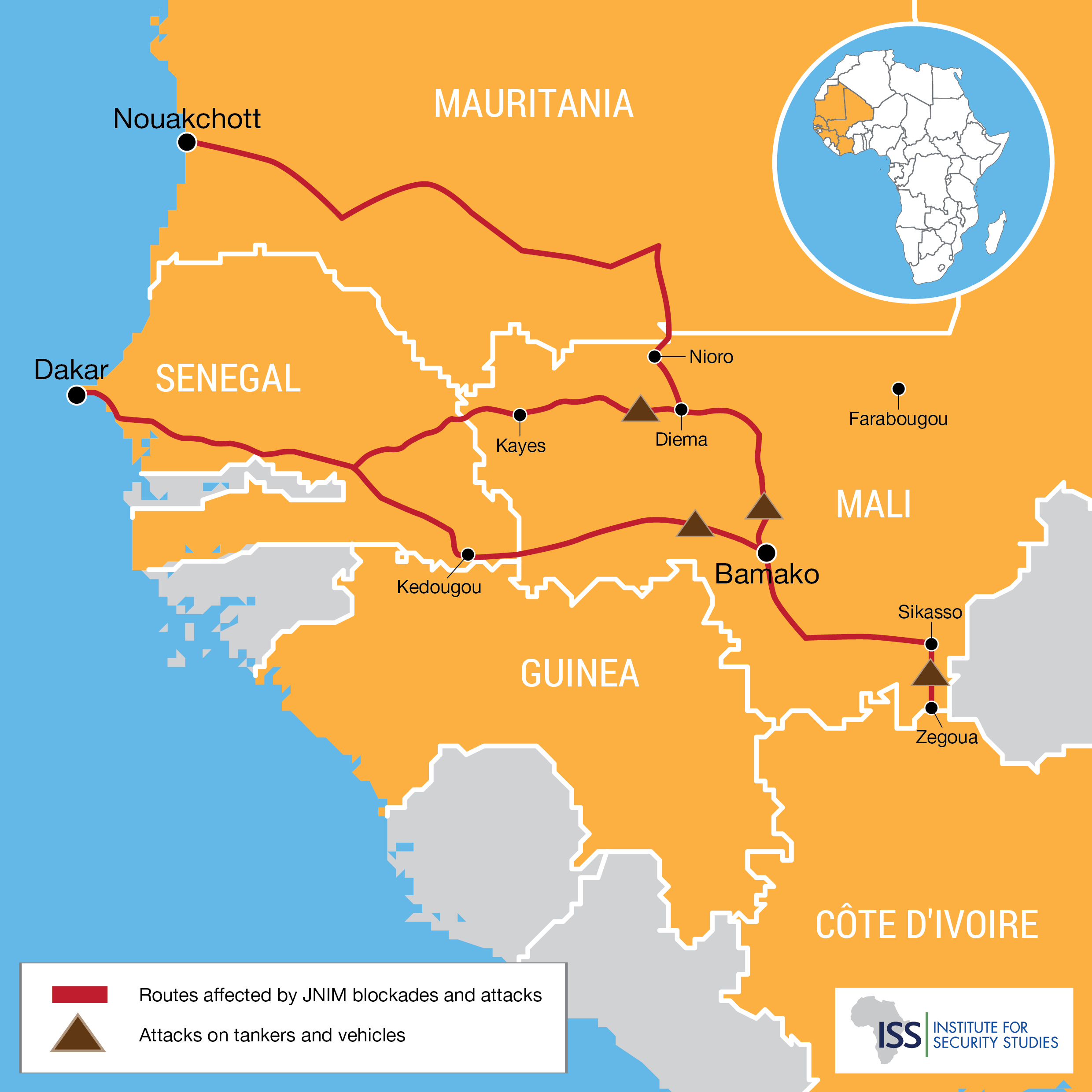
Since 3 September, the al-Qaeda-affiliated Jama’at Nusrat al-Islam wal-Muslimin (JNIM) has been obstructing traffic on the strategic roads linking Mali to Senegal and Mauritania. The terrorist group is carrying out its threat to blockade the cities of Kayes and Nioro in retaliation for the local populations’ alleged support for the Malian army.
Despite counter-efforts by the authorities, the roadblocks continue. Along with occasional blockades, several tankers and buses were set alight between 3 and 14 September, and travellers were kidnapped on the routes to Senegal and Mauritania. The road linking Bamako to Côte d’Ivoire was also targeted between the towns of Zégoua and Sikasso. Militants have set three fuel tanks alight.
Fearing bombings by Malian Armed Forces (FAMa) aircraft, the jihadists abandoned some roadblocks to hide in wooded areas and carry out surprise attacks on convoys of vehicles. Trade with Senegal, Mauritania and Côte d’Ivoire – Mali’s source of essential products such as fuel – has been disrupted.
|
Routes and areas targeted by JNIM
|
JNIM began using blockades in 2020, first targeting the city of Farabougou, northeast of Bamako. Since then, several villages in the area have also faced roadblocks, depriving inhabitants of essential services, including food, water, electricity and communication.
To establish a blockade, terrorists take control of the main roads leading to the target locality and set up roadblocks to prevent entry and exit. Residents are prohibited from cultivating their fields during the rainy season and obtaining supplies from other localities. The resulting price increases make living conditions difficult, forcing people to either flee or work with jihadists as a resilience strategy.
JNIM also generates revenue through the informal taxes it levies on populations in exchange for protection services, as well as the sale of stolen livestock. JNIM fighters also target foreign industrial sites whose owners are forced to pay for the safeguarding of their premises. Since June, seven foreign industrial sites, including six Chinese premises, have been attacked in central and western Mali.
JNIM’s blockades have three objectives. First, they punish civilians who resist the jihadists or collaborate with armed forces in the fight against terrorism. This modus operandi enables JNIM to exert indirect control over new territories without having to conquer them militarily.
Second, the blockades aim to publicly discredit the armed forces and pressure the government by showing the army’s inability to secure vital transport routes. Third, blocking the roads to Bamako since 3 September is intended to suffocate the country’s capital. The targeting of fuel tankers from Senegal and Côte d’Ivoire is aimed at paralysing economic activity in Bamako and Mali as a whole.
If fuel shortages persist, they could trigger unrest, destabilising Mali’s transitional authorities
If the fuel shortage in some areas persists, it could trigger social and political unrest, destabilising Mali’s transitional authorities. By exerting this pressure, JNIM is trying to force the government to the negotiating table to secure access for trucks supplying essential goods. It also hopes to restrict the movement of armed forces, thereby creating a security vacuum that favours the mobility and activities of JNIM fighters.
Mali’s authorities have taken several measures to break the blockades, including working to secure the transport corridors used to supply Bamako and other localities.
FAMa launched a vast ground and air operation on 6 September in the Diéma, Nioro and Kayes areas. Army spokesman Colonel-Major Souleymane Dembélé said several terrorist strongholds were destroyed and dozens of insurgents neutralised. From 10 September, FAMa introduced patrols and escorts on various strategic routes, enabling several fuel tankers and civilian vehicles from neighbouring countries to reach Bamako.
On 16 September, during a meeting with the Group of Malian Petroleum Professionals, Prime Minister General Abdoulaye Maïga announced large-scale measures to secure supply routes. He said the state would deploy all necessary means to protect the convoys.
The threat of Mali’s economic collapse will be a test for the Alliance of Sahel States’ unified force
However, the attacks continue. On 21 September, three tankers were ambushed and set on fire between Sikasso and Bamako, on the road to Côte d'Ivoire. Two Ivorian drivers and an apprentice were killed.
With JNIM seemingly betting on success through attrition, are convoy escorts sustainable in the long term? This costly and challenging option requires significant logistical resources, including armoured vehicles and fuel, as well as large numbers of personnel. It can only be implemented simultaneously on several roads for a limited period.
The only realistic solution for Mali’s military is to keep JNIM fighters away from strategic supply corridors and industrial zones. A priority should be to dislodge them from forests and areas adjacent to roads and industrial sites.
The threat of economic collapse hanging over Mali will be a test for the Alliance of Sahel States (AES). The Mali-Niger-Burkina Faso coalition’s unified force of 5 000 soldiers was declared operational on 30 September by Niger’s President Abdourahamane Tchiani. In fact, JNIM could, if successful, use a similar strategy against Burkina Faso and Niger.
Mali’s neighbouring countries also need to help curb this risk. Considering that ports in Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Senegal and Mauritania depend heavily on Malian traffic, the security of consumers, traders and commercial flows to Bamako and other cities in the country must be discussed.
So far, none of Mali’s neighbours have officially reacted to the blockades. All five countries must transcend their political differences in favour of security cooperation against a threat to their economies and stability.
Exclusive rights to re-publish ISS Today articles have been given to Daily Maverick in South Africa and Premium Times in Nigeria. For media based outside South Africa and Nigeria that want to re-publish articles, or for queries about our re-publishing policy, email us.

